Microsoft’s Quantum Chip Breakthrough Signals
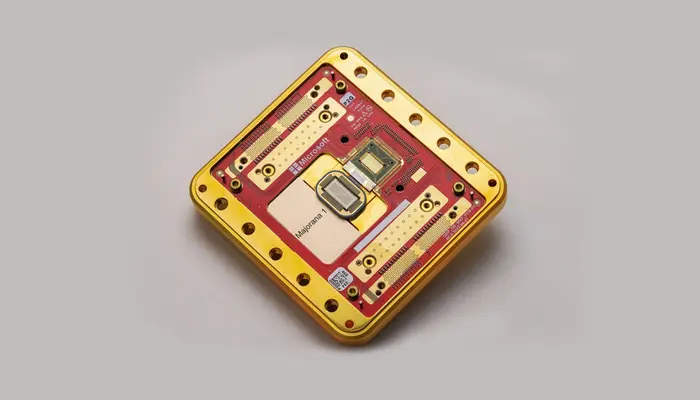

Quantum computing is advancing at a rapid pace, and Microsoft’s latest quantum chip breakthrough has brought the reality of encryption vulnerabilities closer than ever. On February 19, Microsoft introduced Majorana 1, a revolutionary hardware chip that paves the way for quantum computers capable of breaking current encryption protocols within years, not decades.
This development marks a significant leap toward large-scale quantum computing, with the potential to solve complex industrial and societal problems. However, it also raises urgent concerns about data security, as quantum computers could render encryption methods like RSA and AES obsolete. Organizations must act now to adopt post-quantum cryptography before their sensitive data becomes vulnerable.
Quantum Computing Advances Faster Than Expected
Microsoft’s breakthrough accelerates the race toward a one-million-qubit quantum computer, a system capable of solving problems beyond the reach of all existing computers combined. The Majorana 1 chip is built using a Topological Core architecture, featuring the first-ever topoconductor—a new state of matter that enhances stability and efficiency in quantum systems.
Unlike classical computing, where a bit represents either 0 or 1, a qubit exists in a superposition of both states, enabling quantum computers to process data at unparalleled speeds. Microsoft emphasizes that achieving a million-qubit system will unlock unprecedented computational power, making it critical for organizations to upgrade their cybersecurity strategies.
Read: AI Cracks Superbug Resistance in Just Two Days
Cybersecurity Risks: ‘Harvest Now, Decrypt Later’ Attacks
The rise of quantum computing presents an imminent threat to data security. Malicious actors are already stockpiling encrypted data, anticipating the day when quantum computers can instantly decrypt previously secure information. This strategy, known as “harvest now, decrypt later”, underscores the urgent need for quantum-resistant encryption.
Iain Beveridge, Senior Product and Solutions Manager at Entrust, warned that Microsoft’s announcement validates concerns within the cybersecurity industry. “Quantum computing is coming faster than many expect, and organizations must prepare now to protect their data,” he stated.
Failure to transition to post-quantum cryptography could leave businesses, governments, and financial institutions exposed to catastrophic data breaches.
Transitioning to Quantum-Secure Encryption
In August 2024, the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) formalized the first post-quantum cryptography standards. These include three quantum-resistant algorithms designed to secure data, authenticate identities, and establish safe key exchanges over public channels.
NIST urges organizations to begin the transition now, before quantum computers become powerful enough to crack existing encryption. However, a 2024 Entrust Cybersecurity Institute report identified key challenges:
- Lack of clear ownership over cryptographic transitions.
- Limited visibility of cryptographic assets within organizations.
The financial sector is leading the way in adopting quantum-secure solutions. In September 2024, UK-based HSBC successfully tested quantum-secure technology for buying and selling tokenized gold, marking a major milestone in secure financial transactions.
Preparing for the Quantum Future
The arrival of quantum computers is no longer a distant possibility—it is an imminent reality. Microsoft’s Majorana 1 chip is proof that quantum breakthroughs are accelerating, and organizations must adapt before it’s too late.
With encryption protocols at risk, businesses and governments must take proactive steps to integrate post-quantum cryptography, ensuring their data remains secure in the quantum era.
Follow us on Google News, Instagram, YouTube, Facebook,Whats App, and TikTok for latest updates